Introduction
Your eyes do more than help you see—they are a window into your overall health. From subtle changes in color to sudden vision disturbances, your eyes can reveal early warning signs of serious medical conditions. Many people ignore these signals, assuming minor issues are harmless. However, timely detection can be life-saving.
Medical research has shown that eye symptoms often precede systemic diseases, including diabetes, hypertension, liver problems, neurological disorders, and autoimmune conditions. By understanding what your eyes are communicating, you can take proactive steps to protect your vision and general health.
This article explores eight critical eye warning signs, detailing causes, risk factors, preventive measures, and when to seek immediate medical care.
1. Sudden Blurred Vision
What It Looks Like
Blurred vision can appear in one or both eyes, sometimes suddenly or gradually. Objects may seem out of focus, distorted, or hazy.
Possible Causes
-
Stroke – Sudden vision changes can indicate a stroke affecting the occipital lobe or optic nerve. Symptoms may include weakness, numbness, and difficulty speaking.
-
Severe Hypertension – High blood pressure can damage blood vessels in the retina, leading to hypertensive retinopathy and sudden blurriness.
-
Uncontrolled Diabetes – Rapid changes in blood sugar can cause the lens of the eye to swell, temporarily blurring vision.
Real-Life Example
A 52-year-old man noticed sudden blurriness in his right eye. Initially dismissing it, he later experienced weakness in his left arm. A hospital visit revealed he had suffered a minor stroke. Early intervention helped prevent permanent vision loss.
Prevention and Action
-
Monitor blood pressure and blood sugar levels.
-
Schedule regular eye exams, especially if you have risk factors.
-
Seek immediate medical care if sudden blurring occurs.
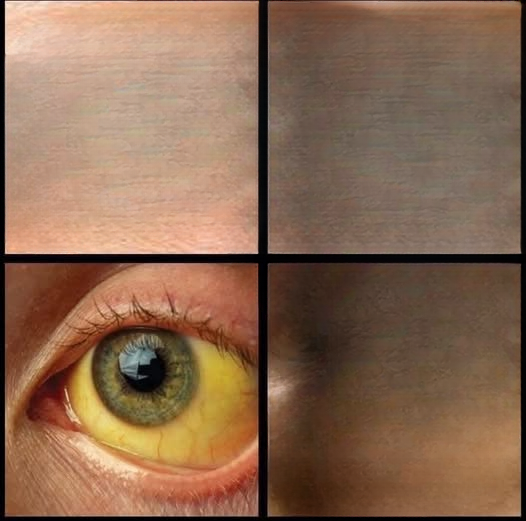
2. Yellowing of the Eyes
What It Looks Like
The whites of your eyes (sclera) turn yellow, sometimes accompanied by dark urine or pale stools.
Possible Causes
-
Jaundice – Accumulation of bilirubin due to liver malfunction.
-
Hepatitis – Viral infections affecting liver function.
-
Liver Damage – Alcohol abuse, cirrhosis, or fatty liver disease can cause yellow eyes.
-
Gallstones – Obstruction of bile ducts may also lead to jaundice.
Why It Matters
Yellow eyes indicate liver stress or damage. Early detection allows for interventions such as lifestyle changes, medication, or in severe cases, surgery.
Case Study
A 34-year-old woman noticed yellowing of her eyes and fatigue. Blood tests confirmed hepatitis A, and she received prompt antiviral treatment. Her liver function improved within weeks, highlighting the importance of early recognition.
Prevention and Action
-
Limit alcohol consumption.
-
Maintain a healthy diet and weight.
-
Vaccinate against hepatitis A and B where appropriate.
-
See a doctor immediately if yellowing appears.
3. Loss of Peripheral Vision
What It Looks Like
Peripheral vision loss may feel like looking through a tunnel, where side vision is impaired while central vision remains intact.
Possible Causes
-
Glaucoma – Increased intraocular pressure damages the optic nerve. Often asymptomatic until advanced stages.
-
Retinal Disorders – Detachment or retinal diseases can cause vision loss on one or both sides.
-
Neurological Issues – Brain injuries or strokes affecting visual pathways.
Real-Life Example
A 60-year-old woman noticed difficulty seeing objects to her left. A thorough eye exam diagnosed early-stage open-angle glaucoma. Immediate treatment with eye drops preserved her vision.
Prevention and Action
-
Annual eye exams, especially after age 40.
-
Monitor eye pressure and family history of glaucoma.
-
Seek urgent medical attention if peripheral vision loss appears suddenly.
4. Dark Spots, Flashes, or Curtain-Like Vision
What It Looks Like
-
Seeing floating black spots or “floaters.”
-
Flashes of light.
-
A shadow or “curtain” across part of your visual field.
Possible Causes
-
Retinal Detachment – Separation of the retina from its supporting tissue can cause permanent vision loss if untreated.
-
Retinal Tear or Hole – Can lead to detachment.
-
Migraine Auras – Brief flashes may occur but are usually accompanied by headaches.
Real-Life Example
A 47-year-old man reported seeing flashes and a dark curtain over his vision. Immediate evaluation revealed a retinal detachment. Surgery successfully reattached the retina, preserving most of his vision.
Prevention and Action
-
Avoid delaying care for sudden flashes or floaters.
-
Regular eye exams help detect early retinal changes, especially in nearsighted individuals.
5. Bulging Eyes
What It Looks Like
Eyes that protrude or appear unusually large.
Possible Causes
-
Hyperthyroidism / Graves’ Disease – Overactive thyroid can cause eye bulging and irritation.
-
Orbital Tumors – Masses behind the eyes can push them outward.
-
Inflammatory Conditions – Rare infections or orbital cellulitis may lead to swelling.
Signs and Symptoms
-
Irritation or redness.
-
Double vision.
-
Sensitivity to light.
Real-Life Example
A 38-year-old woman with bulging eyes, anxiety, and weight loss was diagnosed with Graves’ disease. Treatment with antithyroid medication and monitoring of eye health improved her symptoms.
Prevention and Action
-
Regular thyroid checkups if at risk.
-
Seek ophthalmologic evaluation for unexplained bulging.
6. Unequal Pupil Sizes (Anisocoria)
What It Looks Like
One pupil is noticeably larger than the other, unrelated to light changes or eye drops.
Possible Causes
-
Neurological Disorders – Stroke, brain tumors, or aneurysms affecting nerves controlling the pupil.
-
Trauma – Head or eye injuries.
-
Medical Conditions – Certain infections or medications.
Real-Life Example
A 29-year-old man noticed one dilated pupil after a minor fall. Emergency imaging revealed a small brain aneurysm. Early treatment prevented rupture and serious complications.
Prevention and Action
-
Immediate medical evaluation for sudden anisocoria.
-
Neurological assessment if accompanied by headache, weakness, or vision changes.
7. Extreme Dryness and Persistent Redness
What It Looks Like
Chronic irritation, redness, burning sensation, or feeling like sand in your eyes.
Possible Causes
-
Autoimmune Disorders – Sjögren’s syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, lupus.
-
Chronic Dry Eye Syndrome – Tear production issues.
-
Allergic or Environmental Factors – Dust, smoke, or prolonged screen use.
Real-Life Example
A 52-year-old woman experienced constant eye redness and dryness. Evaluation revealed Sjögren’s syndrome. Treatment with artificial tears and systemic therapy reduced discomfort.
Prevention and Action
-
Regular eye checkups.
-
Proper hydration and environment control.
-
Evaluation for underlying autoimmune disorders if symptoms persist.
8. Double Vision (Diplopia)
What It Looks Like
Seeing two images of a single object, which may appear horizontally, vertically, or diagonally.
Possible Causes
-
Nerve Damage – Cranial nerve palsies affecting eye muscles.
-
Multiple Sclerosis – Demyelination can interfere with coordinated eye movements.
-
Aneurysms or Stroke – Sudden nerve compression may lead to diplopia.
-
Muscle Disorders – Myasthenia gravis can weaken eye muscles.
Real-Life Example
A 45-year-old man noticed sudden double vision and drooping eyelids. Neurological evaluation diagnosed a cranial nerve palsy secondary to high blood pressure. Prompt treatment prevented further complications.
Prevention and Action
-
Immediate evaluation for sudden double vision.
-
Regular eye and neurological exams for persistent or recurring symptoms.
How to Maintain Eye Health
-
Regular Eye Exams – Early detection of glaucoma, retinal issues, and systemic disease indicators.
-
Control Blood Pressure and Blood Sugar – Reduces risk of vision-threatening complications.
-
Healthy Diet – Rich in vitamins A, C, E, and omega-3 fatty acids.
-
Protect Eyes from UV Exposure – Wear sunglasses and hats outdoors.
-
Avoid Smoking – Smoking increases the risk of macular degeneration and cataracts.
-
Manage Screen Time – Follow the 20-20-20 rule to reduce eye strain.
-
Hydrate and Rest Eyes – Proper hydration supports tear production and eye comfort.
Conclusion
Your eyes communicate critical information about your health. Sudden blurred vision, yellowing, peripheral vision loss, flashes, bulging eyes, unequal pupils, extreme dryness, and double vision are not to be ignored.
Key Takeaways:
-
Early recognition can save sight and lives.
-
Seek prompt medical attention for any of these warning signs.
-
Regular eye exams and proactive health management are essential.
Your vision is a reflection of your overall well-being. By paying attention to these eye warning signs, you can detect serious conditions early, improve treatment outcomes, and protect both your sight and health.