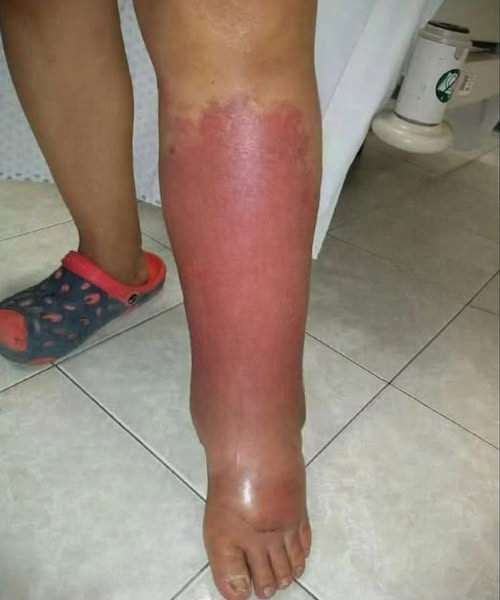
Swollen feet are a common concern experienced by people of all ages. For some, the swelling appears after standing for long hours, while for others it may occur suddenly and without an obvious trigger. In most cases, mild swelling is temporary and harmless. However, when it persists, worsens, or is associated with other symptoms, it can indicate an underlying health issue.
Understanding the possible causes of swollen feet, knowing how to manage them, and recognizing when to seek professional care are all important for protecting overall health. This comprehensive guide explores the wide range of reasons feet may swell, prevention strategies, and steps people can take to improve circulation and comfort.
What Is Foot Swelling?
Foot swelling, medically referred to as peripheral edema, occurs when excess fluid builds up in the tissues of the lower body. The feet and ankles are particularly prone to this because gravity naturally pulls fluids downward when a person is standing or sitting for extended periods.
Swelling can be localized—affecting only one foot or ankle—or generalized, impacting both feet. Localized swelling is often linked to an injury or infection, while generalized swelling may relate to systemic conditions like heart, liver, or kidney issues.
Common Causes of Swollen Feet
1. Prolonged Standing or Sitting
One of the most common, everyday causes of swollen feet is simply standing or sitting for too long. People who work in jobs that require long hours on their feet—such as nurses, retail employees, or factory workers—often notice their shoes feel tighter by the end of the day. Similarly, long periods of sitting, such as during a lengthy flight, can cause fluid to pool in the lower extremities.
2. Injuries and Sprains
A twisted ankle, a minor fracture, or even a stubbed toe can result in immediate swelling. This happens because the body increases blood flow and sends immune cells to the injured area to promote healing.
3. Pregnancy
Swollen feet are very common during pregnancy, particularly in the third trimester. Hormonal changes and increased pressure from the growing uterus affect circulation and lead to fluid retention in the legs and feet.
4. Medications
Certain medications may cause fluid retention as a side effect. These include:
-
Blood pressure medicines (calcium channel blockers)
-
Steroids
-
Antidepressants
-
Hormone therapies
If swelling develops after starting a new medication, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional.
5. Medical Conditions
Persistent foot swelling can sometimes indicate more serious health concerns, such as:
-
Heart disease: Reduced pumping efficiency may cause fluid buildup.
-
Kidney disease: Impaired kidney function can prevent the body from eliminating excess fluid.
-
Liver disease: Conditions such as cirrhosis can contribute to swelling in the legs and feet.
-
Venous insufficiency: Weak or damaged veins struggle to return blood to the heart, leading to pooling in the legs.
Lifestyle and Environmental Triggers
Heat and Weather Conditions
Many people notice their feet swell in hot weather. Warm temperatures dilate blood vessels, making it easier for fluid to leak into surrounding tissues.
Diet and Salt Intake
Eating foods high in sodium can cause the body to retain water, leading to noticeable swelling in the extremities. Processed foods, fast food, and salty snacks are common culprits.
Dehydration
Ironically, not drinking enough water can also cause fluid retention. When the body senses dehydration, it may hold onto fluids as a protective response.
Prevention Strategies
Stay Active
Movement helps stimulate circulation and prevents fluids from pooling in the lower body. Even light activities such as walking, stretching, or flexing the feet during a desk job can make a big difference.
Elevation
Lifting the feet above heart level for short periods encourages fluid to flow back toward the torso, reducing swelling.
Compression Wear
Compression socks or stockings gently squeeze the feet and legs, improving circulation and limiting swelling. They are especially useful for frequent travelers or those who stand for long periods.
Balanced Diet
Maintaining a diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while limiting excess sodium helps the body maintain healthy fluid balance.
Hydration
Drinking adequate amounts of water supports kidney function and reduces the likelihood of fluid retention.
When to Seek Medical Help
While occasional mild swelling is not usually a cause for concern, it is important to consult a healthcare provider if:
-
Swelling is sudden and severe.
-
It occurs in only one foot and is accompanied by pain or redness.
-
There are additional symptoms such as shortness of breath, chest pain, or fever.
-
Swelling does not improve with rest and lifestyle changes.
These signs may point to conditions that require medical evaluation, such as blood clots, infections, or organ-related issues.
Emotional and Quality-of-Life Impacts
Swollen feet may seem like a purely physical concern, but they can affect emotional well-being as well. Chronic swelling can make walking uncomfortable, limit footwear choices, and reduce mobility. Over time, this may contribute to frustration, reduced self-confidence, or social withdrawal.
Taking steps to manage swelling not only improves physical health but also helps individuals feel more in control of their daily lives.
Broader Health Awareness
Foot swelling can serve as a useful reminder to pay attention to overall wellness. Since the feet are at the farthest point from the heart, they often reveal early signs of circulatory or systemic problems. Staying alert to changes in the feet can encourage timely medical checkups and preventive care.
Conclusion
Swollen feet are a common condition with a wide variety of causes, ranging from harmless lifestyle factors to serious medical concerns. By understanding potential triggers, practicing preventive strategies, and knowing when to seek medical help, individuals can protect their health and maintain a better quality of life.
Ultimately, while swelling may sometimes be dismissed as a minor nuisance, it can provide valuable insight into the body’s overall condition. Listening to those signals and responding appropriately is an important part of staying healthy.