Have you ever noticed veins suddenly standing out on your hands, arms, legs, or even your chest? For most people, this phenomenon is perfectly normal. Veins, the vessels responsible for returning blood to the heart, can become more visible due to a variety of factors—from natural aging and genetics to temporary changes in your body. While prominent veins are often harmless, understanding the reasons behind their appearance is essential, especially when they might signal underlying health issues.
Section 1: Natural Causes of Prominent Veins
1. Aging and Skin Changes
As we grow older, our skin naturally loses elasticity and becomes thinner. This process reduces the layer of tissue covering veins, making them easier to see. Many older adults notice that veins in their hands, forearms, or legs appear more pronounced than they did in youth.
2. Low Body Fat
Individuals with low body fat often have more visible veins because there is less subcutaneous fat to cover them. Fitness enthusiasts, especially those with lean muscle mass, may see veins pop up more frequently on their arms, legs, and abdomen.
3. Physical Activity
Exercise, particularly strength training and weightlifting, increases blood flow to muscles. This process, known as the “vascular pump,” temporarily pushes veins closer to the surface, making them more prominent. Cardiovascular activities like running or cycling can also have a similar effect, especially during intense exertion.
4. Heat and Environmental Factors
Heat causes veins to expand, or dilate, to help regulate body temperature. On hot days or after a warm shower, you might notice your veins becoming more visible. This effect is temporary and usually harmless.
5. Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations can influence vein visibility. Pregnancy, menopause, or hormone therapy can all affect circulation and the elasticity of veins. Many women notice increased vein prominence during these periods due to elevated blood volume and hormonal shifts.
Section 2: When Veins Might Signal a Medical Concern
While most visible veins are harmless, certain patterns or associated symptoms may indicate underlying conditions.
1. Circulation Problems
Sudden appearance of veins without an obvious cause—like exercise or weight loss—can point to circulation issues. Poor circulation may result from conditions such as chronic venous insufficiency, where veins struggle to return blood efficiently to the heart.
2. Pain, Swelling, or Redness
If veins are accompanied by pain, swelling, or redness, this could suggest inflammation or even a blood clot. Superficial thrombophlebitis, for example, occurs when a vein becomes inflamed, causing tenderness and a firm, rope-like appearance.
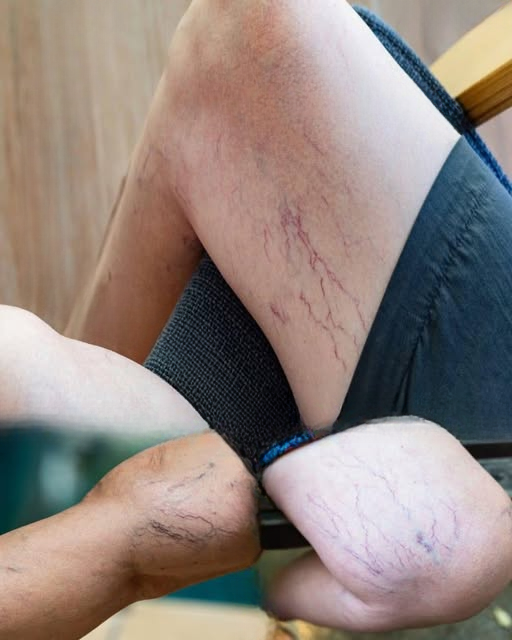
3. Varicose Veins
Varicose veins are hard, twisted, and sometimes bulging veins, usually in the legs. They result from weakened vein walls or faulty valves, causing blood to pool rather than flow efficiently. Common symptoms include aching, heaviness, and visible swelling.
4. Skin Changes Around Veins
Discoloration, itching, or the development of ulcers near veins can indicate chronic venous insufficiency. These symptoms suggest long-term pressure in the veins that may require medical intervention.
5. Veins on Chest or Abdomen
Rarely, visible veins in unusual areas like the chest or abdomen may be linked to serious conditions such as liver disease or cancer. Web-like patterns, called “caput medusae,” can sometimes be associated with portal hypertension, a complication of liver problems.
Section 3: Understanding Varicose Veins and Spider Veins
1. Varicose Veins
Varicose veins are more than a cosmetic concern—they can signal impaired circulation. Common contributing factors include genetics, age, obesity, pregnancy, and prolonged standing. In some cases, medical treatment may be necessary to reduce symptoms or prevent complications like blood clots.
2. Spider Veins
Smaller than varicose veins, spider veins appear as fine, web-like clusters of red, blue, or purple vessels near the skin’s surface. They are typically harmless but can be bothersome cosmetically. Risk factors include hormonal changes, sun exposure, and genetics.
Section 4: Risk Factors That Make Veins More Prominent
-
Genetics: A family history of prominent veins or varicose veins increases likelihood.
-
Sedentary Lifestyle: Prolonged sitting or standing can increase pressure in leg veins.
-
Obesity: Excess weight puts additional strain on veins, reducing efficiency of blood return.
-
Pregnancy: Hormonal changes and increased blood volume can stretch veins, causing temporary or long-term visibility.
Understanding these risk factors can help individuals take preventive measures or seek early consultation with a healthcare professional.
Section 5: Prevention and Lifestyle Adjustments
1. Exercise Regularly
Engaging in physical activity—especially leg-strengthening exercises like walking, swimming, or cycling—can improve circulation and reduce venous pressure.
2. Maintain Healthy Body Weight
Excess weight increases pressure on veins, particularly in the legs. Maintaining a balanced diet and healthy weight helps reduce strain.
3. Avoid Prolonged Sitting or Standing
Take breaks to move around and elevate legs periodically to promote blood flow. Compression stockings can also aid circulation in at-risk individuals.
4. Skin Care
Moisturizing regularly keeps skin healthy and elastic, helping maintain the appearance of veins and reducing risk of irritation around varicose veins.
5. Monitor Changes
Keep track of any new or worsening vein visibility, discomfort, or skin changes. Early detection of circulation issues can prevent serious complications.
Section 6: When to Seek Medical Advice
Consult a healthcare professional if you notice:
-
Veins that appear suddenly without an obvious cause.
-
Pain, swelling, warmth, or redness around veins.
-
Hard, twisted, or rope-like veins.
-
Skin discoloration, ulcers, or itching near veins.
-
Veins on unusual areas such as the chest or abdomen.
-
Other symptoms like fatigue, shortness of breath, or swelling in multiple body parts.
Early evaluation can identify circulation problems, blood clots, or other serious conditions before they worsen.
Section 7: Medical Treatments for Vein Problems
1. Compression Therapy
Medical-grade compression stockings improve blood flow and reduce swelling.
2. Minimally Invasive Procedures
-
Sclerotherapy: A solution is injected to close small varicose or spider veins.
-
Laser Therapy: Light energy targets veins, causing them to fade over time.
3. Surgical Options
For severe varicose veins, procedures like vein stripping or ligation may be recommended to remove damaged veins.
4. Medications
In some cases, medications that improve vein tone or manage inflammation can complement other treatments.
Section 8: The Psychological Impact of Visible Veins
While often considered a cosmetic issue, prominent veins can affect self-esteem and confidence. Patients may experience:
-
Embarrassment in social or professional settings.
-
Anxiety about potential health implications.
-
Avoidance of certain clothing or activities to hide veins.
Addressing vein concerns early—whether through lifestyle changes, medical consultation, or treatment—can improve both physical health and mental well-being.
Section 9: Vein Visibility in Different Populations
-
Athletes: Increased blood flow and low body fat make veins more prominent.
-
Pregnant Women: Hormonal changes and increased blood volume often cause temporary vein prominence.
-
Elderly Individuals: Thinner skin and decreased elasticity naturally reveal veins.
Recognizing normal variations in vein visibility helps distinguish between benign causes and those requiring medical attention.
Section 10: Global Perspectives on Vein Health
Medical professionals worldwide emphasize awareness campaigns and preventive strategies:
-
Early recognition of varicose veins and circulation problems.
-
Education on lifestyle modifications and exercise.
-
Access to minimally invasive treatments to reduce complications.
Raising awareness helps prevent serious consequences such as deep vein thrombosis, chronic venous insufficiency, or vascular ulcers.
Conclusion: Knowing Your Veins and Protecting Your Health
Visible veins are often a normal part of life, influenced by age, genetics, fitness level, and environmental factors. For most people, they are harmless and purely cosmetic.
However, sudden changes, pain, swelling, or skin abnormalities near veins can indicate more serious health concerns. Paying attention to your body, monitoring changes, and seeking timely medical advice are essential for maintaining vascular health.
By understanding the causes, risks, and preventive measures, individuals can ensure that prominent veins remain a benign feature rather than a sign of deeper health issues. Awareness, vigilance, and proper care are the keys to a healthy circulatory system and peace of mind.